Enable Nested Virtualization on QNAP QTS
Cause
The Virtualization Station (QVS) of QNAP QTS is really useful to setup your personal VMs. But when you want to establish a testing environment that starts a few VMs inside a VM with automation tools, you may find out the nested virtualization (or maybe called “nested KVM”, “recursive KVM”, “KVM on KVM”, etc.) is default disabled and you cannot enable it through QTS UI.
Take my NAS (of x86_64 architecture) for example, you can see the cpu information through the shell of a VM:
[root@localhost ~]# lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 8
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 8
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 60
Model name: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E3-1246 v3 @ 3.50GHz
Stepping: 3
CPU MHz: 3491.932
BogoMIPS: 6983.86
Hypervisor vendor: KVM
Virtualization type: full
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 8192K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon rep_good nopl eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm invpcid_single tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm xsaveopt
The output lacks the Virtualization: VT-x line.
Also you can check the kernel module parameter through the shell of QTS:
[~] # cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested
N
Manually Enable Nested Virtualization
First of all, make sure you set the cpu type of your instance as “Passthrough”. (Thanks to Kirill’s kind reminder)
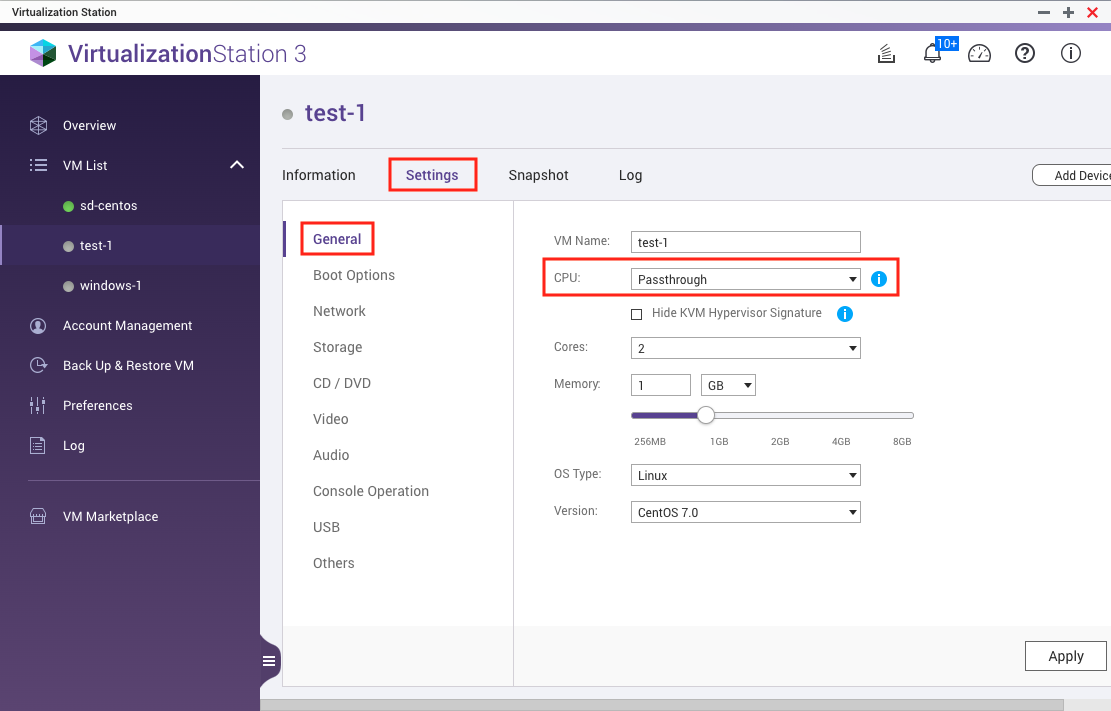
Then, by checking the following file
[~] # vim /share/CACHEDEV1_DATA/.qpkg/QKVM/usr/etc/qvsd.d/44-preload/01-module
we can see how the virtualization station load the KVM kernel module:
load_kvm()
{
___load_module kvm.ko ignore_msrs=1
check_ret
# load kvm module
if [ $VMX_FEATURE -ne 0 ]; then
___load_module kvm-intel.ko
check_ret
elif [ $SVM_FEATURE -ne 0 ]; then
___load_module kvm-amd.ko nested=0
check_ret
elif [ $SVM_FEATURE -ne 0 ]; then
elog "Platform not support KVM"
exit 1
fi
}
So now we have two choices (and we can do them both):
- (Permanent way) Change the argument when loading the module in the above function:
___load_module kvm-intel.ko nested=1But a reboot is required.
- (Instant and temporary way) Manually reload the module:
- Make sure the target module name
[~] # lsmod | grep kvm kvm_intel 148558 10 kvm 420352 1 kvm_intelor
[~] # modprobe -l | grep kvm-intel kvm-intel.ko - Find the exact path of the module
[~] # find / -name "kvm-intel.ko" /lib/modules/KVM/kvm-intel.ko /lib/modules/4.2.8/kvm-intel.koyou may see two ‘kvm-intel.ko’ files and one of them is just a symbolic link:
[~] # ls -la /lib/modules/KVM/kvm-intel.ko lrwxrwxrwx 1 admin administ 21 Feb 2 03:17 /lib/modules/KVM/kvm-intel.ko -> ../4.2.8/kvm-intel.ko - Stop all VMs and reload the module
[~] # rmmod kvm-intel.ko [~] # insmod /lib/modules/KVM/kvm-intel.ko nested=1 [~] # lsmod | grep kvm kvm_intel 148558 0 kvm 420352 1 kvm_intel - Check if it did the trick
[~] # cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested Y [~] # cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/ept Y
- Make sure the target module name
Now we’re done! You will see Virtualization: VT-x in a newly opened VM now.
[root@localhost ~]# lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 8
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 8
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 60
Model name: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E3-1246 v3 @ 3.50GHz
Stepping: 3
CPU MHz: 3491.932
BogoMIPS: 6983.86
Virtualization: VT-x
Hypervisor vendor: KVM
Virtualization type: full
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 8192K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon rep_good nopl eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm invpcid_single tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm xsaveopt

Leave a comment